What Are Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)? Everything You Need to Know
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) are a critical component of the pharmaceutical industry, serving as the core substances responsible for producing therapeutic effects in drugs and medications. Understanding the role of APIs is paramount, as they form the foundation for the development and manufacturing of various medical treatments. This article will delve into the definition, functions, and importance of APIs in the realm of healthcare and pharmaceuticals.
Definition of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
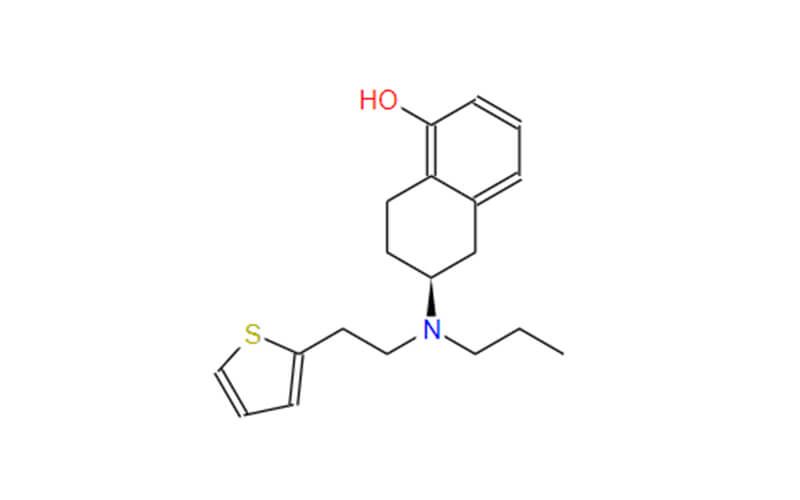
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) refer to the biologically active components of a pharmaceutical drug that produce the desired therapeutic effect in the human body. APIs are the core, pharmacologically active substances in medications, and they are responsible for the drug’s specific therapeutic action. They are often administered in combination with various excipients (inactive substances) to create the final dosage form of a drug, such as tablets, capsules, or liquid formulations.
In essence, APIs are the active substances that interact with biological systems to diagnose, prevent, alleviate, or treat diseases, medical conditions, or symptoms. They can be small chemical compounds, biological molecules (e.g., proteins, antibodies, nucleic acids), or complex mixtures of natural products, depending on the nature of the medication and its intended use. The quality, purity, and potency of APIs are closely monitored and regulated to ensure that pharmaceutical products are safe and effective for patient use.

Types of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
APIs can be classified into two primary categories:
- Synthetic Chemical APIs (Small Molecules):
- Chemically synthesized small molecules.
- Widely used in the pharmaceutical industry, comprising a significant portion of the global market.
- Examples include aspirin and paracetamol.
- Natural Chemical APIs (Biologics):
- Mainly used in biologics, which are large, complex molecules derived from living organisms.
- Gaining popularity, especially in treating complex diseases like cancer and autoimmune disorders.
- Manufactured using biotechnological processes.
Strength and Intermediates of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients:
Active pharmaceutical ingredient manufacturers in China and around the world are obligated to adhere to stringent FDA regulations, specifications, and standardizations. These guidelines are essential for quantifying the quantity of API within each medication, which may vary depending on the specific product and the testing methods employed to ensure its efficacy. According to FDA regulations, the efficacy of each drug must be thoroughly demonstrated before it can be approved for use by patients.
Functions of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) serve several essential functions in the pharmaceutical industry and are crucial for the development and production of medications. Some of their key functions include:
- Therapeutic Action: APIs are primarily responsible for the intended therapeutic action of a drug. They interact with biological systems to treat, alleviate, or prevent a wide range of medical conditions. Whether it’s relieving pain, fighting infection, lowering blood pressure, or addressing chronic illnesses, APIs are designed to bring about a specific therapeutic effect.
- Dosing and Potency: The concentration of an API in a drug formulation determines the dosage strength. Precise control of API content ensures that patients receive the correct amount of the active ingredient required for therapeutic efficacy. This is essential for accurate dosing and to prevent underdosing or overdosing.
- Compatibility and Stability: APIs must remain chemically stable and compatible with excipients to ensure the quality of the final drug product. Proper formulation, storage, and packaging are necessary to maintain API stability over the product’s shelf life.
- Bioavailability: APIs must be formulated in a way that maximizes their absorption and distribution within the body. Various strategies are employed, including solid dispersion, nanoparticle formulations, and prodrugs, to enhance API bioavailability.
Manufacturing of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
The manufacturing of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) is a complex and highly regulated process that involves several key steps. Here is an overview of the API manufacturing process:
- Research and Development (R&D):
API development begins with R&D to discover and design a suitable compound for the desired therapeutic effect.
Medicinal chemistry, synthesis, and optimization are key components of this phase.
- Scale-up and Pilot Plant:
The potential API is scaled up from laboratory quantities to larger pilot plant quantities for further testing and process optimization.
Process parameters are refined during this phase.

- Process Development:
Focuses on developing a scalable and cost-effective manufacturing process for the API.
Parameters include safety, yield, quality, and environmental considerations.
- Manufacturing:
Large-scale API manufacturing occurs in dedicated facilities known as API manufacturing plants.
The process includes chemical synthesis, fermentation (for biopharmaceutical APIs), and isolation/purification.
Quality control and regulatory compliance are essential throughout.
- Quality Control and Testing:
Quality control labs ensure API purity, potency, and safety through analytical chemistry, stability testing, and impurity profiling.
Results are compared to established specifications to meet quality standards.
- Packaging and Labeling:
Once the API passes quality control, it may be packaged in appropriate containers, labeled, and stored for distribution.
- Regulatory Approval:
Regulatory agencies, such as the FDA, assess the manufacturing process, quality control, and safety of the API before approval for use in pharmaceutical products.
- Supply Chain Management:
APIs are distributed to pharmaceutical companies for the formulation of final drug products.
Supply chain management ensures reliable and timely API delivery.
- Continuous Improvement:
API manufacturers focus on continuous process improvement, optimizing yield, reducing waste, and enhancing environmental sustainability.
API manufacturing is highly regulated to ensure patient safety and the efficacy of pharmaceutical products. Compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and other regulatory guidelines is crucial to produce safe and effective APIs for use in medications.
Conclusion
The primary and foremost function of APIs is to ensure that a drug has the intended therapeutic effect on the patient’s body. Any failure to achieve this outcome can pose significant risks to the patient’s well-being, underscoring the vital importance of maintaining both efficacy and quality.
The prevalence of unhealthy lifestyle choices and dietary habits, an aging global population, and various other factors have contributed to a surge in chronic diseases. Moreover, the post-pandemic era has witnessed a sudden upswing in health awareness among specific populations. These combined factors have created a wealth of opportunities for pharmaceutical companies.
Nonetheless, the emphasis on maintaining the quality of APIs remains paramount. Therefore, pharmaceutical API manufacturing companies must engage in continuous innovation and improvement to deliver effective, high-quality medications that enhance the quality of life on a global scale.