The Use of Sugammadex Sodium in Combination with Other Drugs
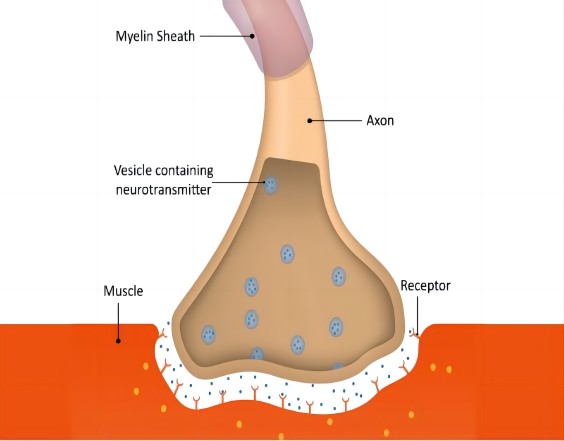
Sugammadex sodium is a reversal agent for neuromuscular blocking drugs (NMBDs) of the steroidal class, such as rocuronium and vecuronium. It is a modified gamma-cyclodextrin that forms a tight, non-covalent complex with steroidal NMBDs, effectively removing them from their receptor sites. This results in a rapid and complete reversal of neuromuscular blockade.
Sugammadex sodium is a relatively new drug, and its interactions with other drugs are still being studied. However, a number of studies have been conducted to investigate the safety and efficacy of sugammadex sodium in combination with other commonly used drugs.
General Considerations of Sugammadex Sodium
Sugammadex sodium is generally safe and well-tolerated when used in combination with other drugs. However, there are a few potential interactions that should be kept in mind.
- Anesthetics: Sugammadex sodium can increase the anesthetic requirements of patients. This is because sugammadex sodium can displace anesthetics from their binding sites on plasma proteins.
- Antibiotics: Some antibiotics, such as aminoglycosides and macrolides, can potentiate the neuromuscular blocking effects of NMBAs. This is because these antibiotics can interfere with the transmission of nerve impulses. It is important to note that sugammadex sodium does not reverse the neuromuscular blocking effects of antibiotics.
- Calcium channel blockers: Calcium channel blockers, such as verapamil and diltiazem, can prolong the duration of action of NMBAs. This is because calcium channel blockers can decrease the release of acetylcholine from nerve terminals. It is important to monitor patients closely for neuromuscular blockade if they are taking calcium channel blockers.
Specific Drug Interactions of Sugammadex Sodium
A number of studies have been conducted to investigate the safety and efficacy of sugammadex sodium in combination with specific drugs. The following are some of the key findings from these studies:
- Opioids
Sugammadex sodium can be safely used in combination with opioids. Opioids do not potentiate or prolong the neuromuscular blocking effects of NMBDs.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAIDs can potentiate the neuromuscular blocking effects of NMBDs. However, sugammadex sodium can still be used to reverse neuromuscular blockade in patients who have received NSAIDs.
- Steroids
Steroids can potentiate the neuromuscular blocking effects of NMBDs. However, sugammadex sodium can still be used to reverse neuromuscular blockade in patients who have received steroids.
- Anticoagulants
Sugammadex sodium can be safely used in combination with anticoagulants. Sugammadex sodium does not affect blood coagulation.
- Other drugs
Sugammadex sodium has also been studied in combination with a variety of other drugs, including insulin, diuretics, anticonvulsants, and antidepressants. No significant interactions have been reported with these drugs.
Additional Interactions of Sugammadex Sodium
In addition to the drug interactions listed above, there are a few other potential drug interactions that should be considered when using sugammadex sodium:
- Digoxin: Sugammadex sodium can increase the serum concentration of digoxin. This is because sugammadex sodium can displace digoxin from its binding sites on plasma proteins. Patients taking digoxin should be monitored closely for signs and symptoms of digoxin toxicity if they are given sugammadex sodium.
- Warfarin: Sugammadex sodium can decrease the serum concentration of warfarin. This is because sugammadex sodium can displace warfarin from its binding sites on plasma proteins. Patients taking warfarin should be monitored closely for signs and symptoms of bleeding if they are given sugammadex sodium.
- Oral contraceptives: Sugammadex sodium can decrease the effectiveness of oral contraceptives. This is because sugammadex sodium can increase the metabolism of oral contraceptives. Patients taking oral contraceptives should be advised to use a backup method of contraception if they are given sugammadex sodium.
Clinical Implications
The safety and efficacy of sugammadex sodium in combination with other drugs have important clinical implications. For example, sugammadex sodium can be safely used in patients who are taking other drugs that can potentiate or prolong the neuromuscular blocking effects of NMBDs. This is important because it allows clinicians to use NMBDs safely and effectively in a wider range of patients.
Additionally, sugammadex sodium can be used to reverse neuromuscular blockade in patients who have received other drugs that can cause respiratory depression, such as opioids. This is important because it can help to prevent the need for mechanical ventilation in these patients.
Summary
Sugammadex sodium is a valuable tool for anesthesiologists, but it can be expensive. The price of sugammadex sodium varies depending on the country and the vendor. In the United States, the price of a 200 mg vial of sugammadex sodium is approximately $99.74.
The high cost of sugammadex sodium can be a barrier to its use in some settings. However, the benefits of sugammadex sodium often outweigh the costs.
Sugammadex sodium is a valuable tool for anesthesiologists. It is a safe and effective reversal agent for steroidal NMBDs that can be used in combination with a variety of other commonly used drugs. This makes it a versatile and flexible option for anesthesiologists when managing neuromuscular blockade.