The Comparison Between Sugammadex Sodium and Sugammadex
Neuromuscular blockade (NMB) is a medication-induced paralysis that relaxes skeletal muscles. It plays a crucial role in various surgical procedures, allowing for better visualization of the surgical field and facilitating mechanical ventilation. However, ensuring complete reversal of NMB at the end of surgery is essential for patient safety and optimal recovery. Sugammadex sodium is a medication specifically designed to reverse the effects of certain NMB agents, offering advantages over traditional reversal methods.

What is Sugammadex?
Sugammadex is a specific medication designed to reverse the effects of neuromuscular blocking (NMB) drugs. It belongs to a class of compounds called cyclodextrins. Cyclodextrins are cyclic molecules derived from sugar molecules, but with a specific structure that allows them to trap other molecules within their cavity. Sugammadex is a modified version of cyclodextrin, specifically designed to have a high affinity for certain NMB agents.
- Chemical Structure: Sugammadex belongs to a class of compounds called cyclodextrins. These are cyclic molecules derived from natural sugars like starch. However, for use in medicine, sugammadex undergoes specific modifications to enhance its ability to interact with NMB agents.
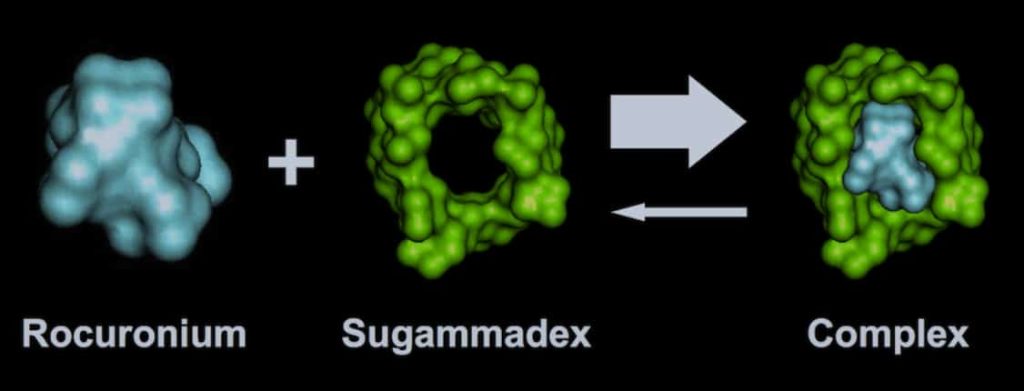
- Mechanism of Action: Sugammadex acts like a molecular “host” with a cavity in its center. This cavity is designed to be a perfect fit for specific NMB agents, acting like a “guest.” When sugammadex encounters an NMB agent in the body, the NMB agent becomes trapped within the sugammadex cavity, forming a complex. This complex formation essentially renders the NMB agent inactive.
- Impact on Neuromuscular Junction: NMB agents work by blocking the transmission of nerve signals to muscles at the neuromuscular junction. By binding the NMB agent and forming an inactive complex, sugammadex effectively removes the NMB agent from its site of action. This allows nerve signals to reach the muscles again, enabling muscle function to return.
- Brand Names: Sugammadex is the scientific name for the molecule itself. However, in clinical settings, it’s always administered in its sodium salt form, called sugammadex sodium. This is because sodium salt is more soluble in water, making it easier to formulate into an injectable solution. Bridion is one of the brand names under which sugammadex sodium is marketed.
Are Sugammadex and Sugammadex Sodium the Same?
While the terms “sugammadex” and “sugammadex sodium” are often used interchangeably, there’s a slight technical difference between the two. Here’s a breakdown for clarity:
Sugammadex: This refers to the core molecule itself, the active ingredient responsible for binding and inactivating NMB agents. It’s the essential component with the specific structure that allows it to interact with NMB drugs.
Sugammadex Sodium: This is the specific form of sugammadex used in clinical practice. Sugammadex, on its own, is not readily soluble in water. To create a medication that can be injected, sugammadex is combined with sodium ions (positively charged particles). This creates a salt form called sugammadex sodium, which is much more soluble in water. This improved solubility allows sugammadex sodium to be easily formulated into a solution for injection, making it suitable for administration in a healthcare setting.
In essence, both terms refer to the same entity used for NMB reversal. However, “sugammadex” refers to the core molecule, while “sugammadex sodium” specifies the specific form used as a medication due to its improved water solubility for injection. For all practical purposes, when discussing the drug used for NMB reversal, you can consider “sugammadex” and “sugammadex sodium” to be synonymous.
Applications of Sugammadex Sodium
Sugammadex sodium is a medication primarily used in anesthesia to reverse the effects of neuromuscular-blocking drugs (NMBDs) such as rocuronium and vecuronium. Its primary application is in surgical procedures where these drugs are used to induce muscle relaxation for intubation or during surgery. Here are some specific applications of sugammadex sodium:
- Anesthesia Reversal: Sugammadex is used to reverse the effects of neuromuscular blockade induced by rocuronium and vecuronium, allowing for the rapid recovery of muscle function at the end of surgery. This is particularly useful in situations where fast reversal of muscle relaxation is desired, such as during emergence from anesthesia.
- Rapid Sequence Intubation (RSI): Sugammadex can be used to rapidly reverse the effects of NMBDs used during RSI, which is a technique used to facilitate endotracheal intubation quickly and effectively in emergency situations or in patients at risk of aspiration.
- Obstetric Anesthesia: Sugammadex can be used in obstetric anesthesia to reverse neuromuscular blockade at the end of surgery, allowing for the rapid recovery of muscle function without delaying the awakening of the mother.
- Bariatric Surgery: In surgeries involving obese patients, sugammadex can be particularly useful due to its ability to rapidly reverse neuromuscular blockade, potentially reducing the risk of postoperative complications associated with prolonged muscle relaxation.
- Reversal of Residual Blockade: Sugammadex can be used to reverse residual neuromuscular blockade, which may occur if NMBDs are not completely metabolized at the end of surgery. Reversing residual blockade can help prevent complications such as impaired respiration and delayed recovery from anesthesia.
- Outpatient Surgery: Sugammadex’s rapid reversal of neuromuscular blockade is advantageous in outpatient surgical settings where quick recovery and discharge of patients are desired.
- Critical Care Medicine: In critical care settings, sugammadex can be used to reverse neuromuscular blockade in patients who require mechanical ventilation, facilitating weaning from the ventilator and early mobilization.
- Reducing Postoperative Complications: By rapidly reversing neuromuscular blockade, sugammadex may help reduce postoperative complications such as residual paralysis, respiratory depression, and postoperative nausea and vomiting.
Advantages of Sugammadex Sodium
Sugammadex sodium offers several advantages over traditional reversal agents like neostigmine in the management of neuromuscular blockade. Some of the key advantages include:
- Rapid Reversal: Sugammadex provides rapid and predictable reversal of neuromuscular blockade within minutes, compared to the relatively slower onset of action of traditional reversal agents like neostigmine.
- Specific Reversal: Sugammadex acts specifically on steroidal non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agents such as rocuronium and vecuronium, forming a complex that is eliminated via renal excretion. This targeted action allows for selective reversal without affecting other physiological systems.
- Reduced Risk of Cholinergic Side Effects: Unlike acetylcholinesterase inhibitors such as neostigmine, sugammadex does not potentiate the effects of acetylcholine, thus avoiding cholinergic side effects such as bradycardia, bronchoconstriction, and excessive salivation.
- Predictable Dosing: Sugammadex’s dose requirement is based on the degree of neuromuscular blockade, making its dosing more predictable and less dependent on patient factors such as weight and renal function compared to traditional reversal agents.
- Lower Risk of Residual Blockade: Sugammadex effectively reverses even deep levels of neuromuscular blockade, reducing the risk of residual paralysis postoperatively, which can lead to complications such as impaired ventilation and delayed recovery.
- Facilitation of Rapid Emergence: The fast reversal provided by sugammadex enables prompt recovery of muscle function at the end of the surgery, allowing for smoother emergence from anesthesia and potentially reducing the time spent in the post-anesthesia care unit (PACU).
- Suitable for Patients with Renal Dysfunction: Sugammadex is primarily eliminated via renal excretion as an unchanged drug, making it suitable for use in patients with renal impairment. In contrast, neostigmine and other acetylcholinesterase inhibitors may accumulate in patients with renal dysfunction, increasing the risk of adverse effects.
- Reduced Need for Anticholinergic Agents: Unlike traditional reversal agents that often require concurrent administration of anticholinergic agents to counteract their side effects, sugammadex does not cause cholinergic effects, thereby reducing the need for additional medications.
- Safe and Well-Tolerated: Sugammadex has been shown to have a favorable safety profile, with minimal adverse effects reported in clinical trials. Its use is associated with a lower incidence of postoperative nausea and vomiting compared to neostigmine.

Considerations for Sugammadex Sodium Use
While sugammadex sodium offers significant advantages, some factors need to be considered when deciding on its use:
- Cost: Sugammadex sodium is typically more expensive than traditional reversal agents. The cost-effectiveness needs to be weighed against the potential benefits for each patient.
- Limited Reversal Spectrum: Sugammadex sodium is only effective in reversing the action of specific steroidal NMB agents like rocuronium and vecuronium. It is not effective for reversing other types of NMB agents.
- Potential Side Effects: Like any medication, sugammadex sodium can cause side effects, although these are typically mild and infrequent. Potential side effects include injection site reactions, allergic reactions, and changes in blood pressure.
- Drug Interactions: Sugammadex sodium can interact with certain medications. It is crucial to inform the healthcare provider about all medications the patient is taking before administering sugammadex sodium.
Example of a Sugammadex Supplier: Qingmu Pharmaceutical
While this article focuses on the clinical applications of sugammadex sodium, it’s important to acknowledge the role of pharmaceutical companies in its development and production. Here, we’ll take a brief look at Qingmu as an example of a potential sugammadex supplier.
Sichuan Qingmu Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., founded in 2011, is a Chinese pharmaceutical company focused on innovation. They are a wholly-owned subsidiary of Chengdu Easton Biopharmaceuticals Co., Ltd. Qingmu specializes in research and development (R&D) and manufacturing of generic active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and advanced intermediates. Additionally, they offer contract development and manufacturing services (CDMO/CMO) for small-molecule chemical drugs.
Conclusion
Sugammadex sodium is a valuable addition to the armamentarium of medications used for reversing NMB. Its rapid and specific action profile offers significant advantages over traditional reversal methods, potentially leading to faster patient recovery, improved airway management, and reduced risk of postoperative complications. However, cost considerations, limited reversal spectrum, and potential side effects need to be taken into account when deciding on its use. Healthcare providers should carefully evaluate the individual patient’s needs and weigh the potential benefits and risks before administering sugammadex sodium.
References
- American Society of Anesthesiologists: Practice Guidelines for Neuromuscular Blockade Update 2018. Anesthesiology. 2018; 129(1): e187-e206. [American Society of Anesthesiologists Neuromuscular Blockade Update]
- Schaller SJ, Fink H. Sugammadex as a reversal agent for neuromuscular block: an evidence-based review. Dove press. 2013; 7: 3623-3633. [Sugammadex as a reversal agent for neuromuscular block]
- Vizcaino R, Payan R, Robledo G, et al. Efficiency and Safety of the Selective Relaxant Binding Agent Sugammadex Sodium for Reversing Rocuronium-Induced Deep Neuromuscular Block: A Single-Center, Open-Label, Dose-Finding, and Phase IIa Study. Anesth Analg. 2021; 133(2): 322-330. [Efficiency and Safety of the Selective Relaxant Binding Agent Sugammadex Sodium]
- Zhang MQ. Discovery, development, and clinical application of sugammadex sodium, a selective relaxant binding agent. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2007; 3(6): 789-799. [Discovery, development, and clinical application of sugammadex sodium]