Understanding Lenvatinib: Mechanism, Side Effects, and Potential Manufacturer
Lenvatinib is a medication specifically designed to combat various types of cancer, including those affecting the thyroid, endometrium, kidney, liver, and lungs. This article delves into the key aspects of lenvatinib, exploring its function, mechanism of action, potential side effects, and other relevant information.
Classification and Primary Function of Lenvatinib
Lenvatinib falls under the category of targeted therapy medications. This classification signifies its ability to specifically target and disrupt the molecular pathways crucial for the growth and survival of cancer cells, unlike traditional chemotherapy drugs that have broader effects on rapidly dividing cells throughout the body.
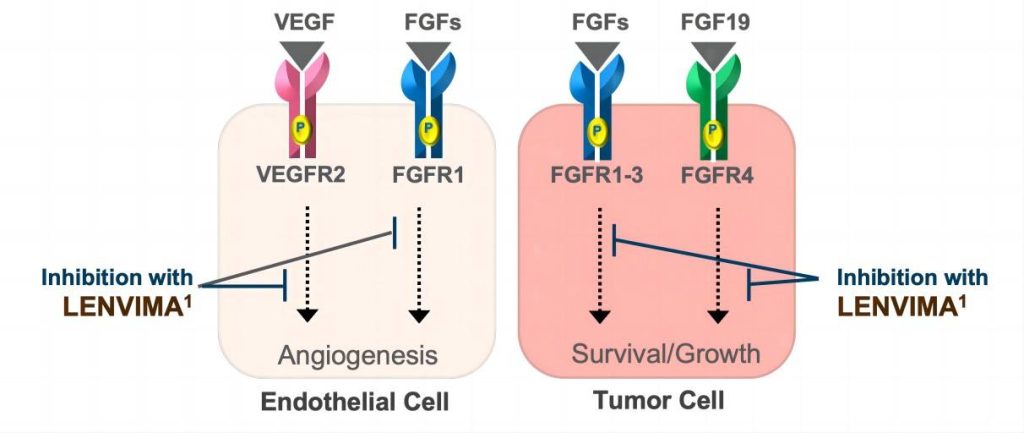
Lenvatinib’s primary function lies in inhibiting angiogenesis, which is the formation of new blood vessels. Tumors are highly dependent on a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients delivered through blood vessels. By effectively blocking the signaling pathways involved in angiogenesis, lenvatinib disrupts the development of new blood vessels, essentially starving the tumor and hindering its ability to grow and spread.
Mechanism Action of Lenvatinib – Targeting Tyrosine Kinases
Lenvatinib’s effectiveness in inhibiting angiogenesis stems from its classification as a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI). These medications exert their effect by targeting specific enzymes called tyrosine kinases. These enzymes play a critical role in various cellular processes, including cell growth, survival, and division.
Lenvatinib acts by binding to specific tyrosine kinases, preventing them from attaching to essential molecules necessary for their activation. This inhibition disrupts the signaling pathways triggered by these kinases, ultimately leading to various consequences for cancer cells, including:
- Reduced cell growth and proliferation: By hindering the activation of pathways essential for cell growth, lenvatinib slows down the uncontrolled division of cancer cells.
- Disrupted cell survival signals: Lenvatinib can also target pathways involved in promoting cancer cell survival, leading to increased cell death.
- Impaired blood vessel formation: As mentioned earlier, lenvatinib specifically targets pathways crucial for angiogenesis, thereby hindering the development of new blood vessels that supply the tumor with nutrients and oxygen.
Potential Side Effects of Lenvatinib
While lenvatinib offers a valuable tool in cancer treatment, it is crucial to acknowledge its potential side effects. Some of the commonly reported side effects associated with lenvatinib include:
- High blood pressure: Lenvatinib can elevate blood pressure levels. Regular monitoring and potential adjustments in medication might be necessary during treatment.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired and lacking energy is a frequent side effect experienced by individuals taking lenvatinib. Adequate rest and addressing any underlying causes of fatigue are essential during treatment.
- Diarrhea: Loose stools or frequent bowel movements can occur with lenvatinib use. Dietary adjustments, fluids, and medications recommended by a healthcare professional can help manage this side effect.
- Weight loss: Unintentional weight loss might be observed while taking lenvatinib. Consulting a healthcare professional regarding dietary strategies and managing any contributing factors is crucial.
- Mouth sores: Painful sores or discomfort in the mouth can occur with lenvatinib use. Maintaining good oral hygiene, using mouthwashes, and seeking professional guidance for severe cases are recommended.
- Skin rash: The development of a rash on the skin is a potential side effect. Reporting this to a healthcare professional and adhering to their recommendations on managing the rash is essential.
What is Lenvatinib Mesilate?
Lenvatinib mesilate plays a crucial role in making lenvatinib readily available and suitable for administration. It is the specific salt form of lenvatinib used in most medications. This form offers significant advantages compared to lenvatinib alone:
- Enhanced water solubility: Lenvatinib mesilate exhibits greater water solubility compared to its parent compound, lenvatinib. This improved characteristic is crucial for formulating the drug into bioavailable medications. Medications with higher water solubility can dissolve more readily in bodily fluids, enabling proper absorption and distribution throughout the body to reach its target site.
- Facilitates formulation: Due to its enhanced water solubility, lenvatinib mesilate allows for the creation of various formulations suitable for different administration methods. These formulations can include tablets, capsules, or solutions for oral administration or injectable solutions for intravenous administration.
- Improved stability: In some cases, salt forms of drugs can offer improved stability compared to the original compound. This can be beneficial for ensuring the medication’s potency and effectiveness throughout its shelf life and during storage.
Therefore, lenvatinib mesilate plays a critical role in transforming the raw compound, lenvatinib, into clinically useful and readily available medications for patients battling various types of cancer.
Lenvatinib: A Member of the Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor (TKI) Family
Lenvatinib drug class belongs to tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), which places it within a broader targeted therapy medication. These medications share a common mechanism of action but differ in their specific targets and clinical applications.
What are TKIs?
TKIs function by targeting and inhibiting the activity of specific enzymes known as tyrosine kinases. These enzymes play a critical role in various cellular processes, including cell growth, differentiation, survival, and migration. By blocking the activity of these enzymes, TKIs can disrupt the uncontrolled growth and proliferation of cancer cells.
Lenvatinib and its TKI Family Members
While TKIs share a common mechanism of action, individual members within this class often have distinct characteristics:
- Specificity: Different TKIs exhibit varying levels of specificity towards different types of tyrosine kinases. This means some TKIs might target a broader range of kinases, while others may be more specific to certain ones. This specificity can influence the therapeutic effects and potential side effects of each TKI.
- Indications: Based on their specific targeting and efficacy, different TKIs are approved for the treatment of various types of cancer. Lenvatinib, for example, is indicated for specific types of thyroid, endometrial, kidney, liver, and lung cancers.
- Side effects: Due to variations in their targets and mechanisms, TKIs can exhibit different side effects profiles. While some side effects might be common across several TKIs, others may be specific to a particular medication.
Examples of Other TKIs:
As mentioned, several other medications fall under the TKI class. Here are some examples:
- Erlotinib and Gefitinib: Primarily used for non-small cell lung cancer and some types of EGFR-positive cancers.
- Imatinib: Known for its effectiveness in chronic myeloid leukemia and gastrointestinal stromal tumors.
- Sunitinib: Approved for the treatment of various cancers, including kidney cancer, gastrointestinal stromal tumors, and neuroendocrine tumors.
Qingmu: A Potential Lenvatinib Manufacturer
However, the landscape of lenvatinib manufacturing is evolving with the emergence of new players. One noteworthy addition is Sichuan Qingmu Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., a Chinese pharmaceutical company that has entered the market as a potential manufacturer of lenvatinib mesilate.
The introduction of new manufacturers like Qingmu can potentially lead to several positive outcomes:
- Increased availability: With additional manufacturers, the overall supply of lenvatinib could potentially increase, improving access to this critical medication for patients in need.
- Potential for cost-effectiveness: Increased competition in the manufacturing space could lead to more competitive pricing, potentially making lenvatinib treatment more affordable for patients and healthcare systems.
- Continuous innovation: The entry of new players can foster innovation within the manufacturing process, potentially leading to improvements in quality, consistency, and formulation development.
Conclusion
Lenvatinib represents a valuable addition to the arsenal available for combatting various types of cancer. By understanding its function, mechanism of action, and potential side effects, individuals and their healthcare providers can make informed decisions regarding treatment options. It is crucial to remember that the information presented here serves as a starting point, and consulting with a qualified healthcare professional is essential for personalized guidance and optimal treatment outcomes.