Understanding Nilotinib Hydrochloride: A Comprehensive Guide
Nilotinib hydrochloride, often shortened to nilotinib, is a potent medication classified as a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI). This article delves into the intricacies of nilotinib, exploring its function, role in treating specific conditions, available forms and dosages, and potential interactions with other medications.
What is Nilotinib API and How it Works
Nilotinib API is the active phamaceutical ingredients of nilotinib.
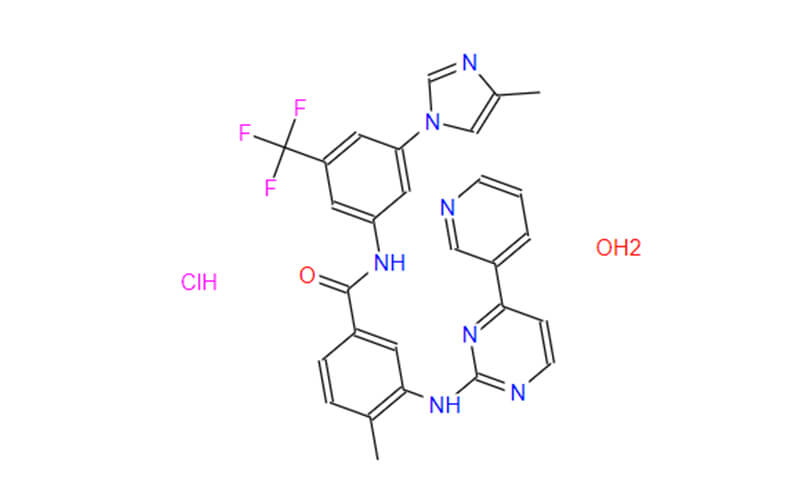
Nilotinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) that serves as the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in the medication Tasigna. This drug is primarily used in the treatment of certain types of leukemia, specifically chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Nilotinib belongs to a class of medications known as BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitors and is designed to target and inhibit the activity of the BCR-ABL fusion protein, which is characteristic of CML.
Here’s how it works:
- Targeting BCR-ABL: CML is caused by a genetic abnormality that results in the formation of a protein called BCR-ABL. This protein acts like an abnormal “on switch” for cancer cells, promoting their uncontrolled growth and division.
- Blocking the Signal: Nilotinib binds to the BCR-ABL protein, acting like a molecular lock and preventing it from sending the “growth” signal to cancer cells. This effectively shuts down the uncontrolled growth process.
- Multiple Targets: Nilotinib also has some activity against other tyrosine kinases, such as c-Kit and PDGF, which can further contribute to its effectiveness in treating CML and potentially other cancers.
- Drug Form: Nilotinib API is not directly administered to patients. It is used as an active ingredient in the formulation of commercial medications such as Tasigna® capsules.
Nilotinib Hydrochloride’s Role in Treating Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML)
Nilotinib hydrochloride, also known by the brand name Tasigna®, belongs to a class of drugs called tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). These drugs work by targeting and blocking the activity of specific enzymes called tyrosine kinases, including the BCR-ABL protein. In CML, nilotinib hydrochloride acts like a molecular lock, fitting snugly onto the BCR-ABL protein and preventing it from sending its growth signals to cancer cells.
Here’s a closer look at nilotinib hydrochloride’s role in treating CML:
- Highly effective: Nilotinib hydrochloride has proven to be highly effective in achieving deep remission and even cure in CML patients, particularly those who are resistant to other TKIs. Studies have shown that it can achieve major molecular response (MMR), a key indicator of successful CML treatment, in a significant proportion of patients.
- Targeted therapy: Unlike traditional chemotherapy, which targets all rapidly dividing cells, nilotinib hydrochloride specifically targets the BCR-ABL protein. This targeted approach minimizes side effects and improves tolerability for patients.
- Convenient administration: Nilotinib hydrochloride comes in capsule form, allowing patients to conveniently take their medication at home. This improves adherence and quality of life compared to treatments requiring injections or hospitalization.
Nilotinib API Available Forms and Dosage
Nilotinib API, also known as nilotinib tosylate monohydrate, is a potent medication used to treat chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML). It acts as a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), specifically targeting the BCR-ABL protein that drives CML cell growth.
Available Forms
Nilotinib API itself is not directly administered to patients. It’s used as an active ingredient in commercially available medications, primarily:
- Tasigna® capsules: These are the most common form of nilotinib, available in three strengths: 50 mg, 150 mg, and 200 mg. The recommended dosage varies depending on the patient’s CML stage, response to treatment, and individual factors.
Dosage
The recommended dosage of nilotinib varies depending on several factors, including:
- Type of CML: The dosage is different for newly diagnosed CML and CML that is resistant or intolerant to other treatments.
- Patient’s age and weight: Dosage adjustments may be necessary for children or adults with certain weight ranges.
- Response to treatment: The doctor may adjust the dosage based on the patient’s response to the medication.
Here’s a general overview of the recommended dosages:
- Newly diagnosed CML:
- Adults: 300 mg twice daily
- Children with body surface area (BSA) < 0.32 m²: 50 mg per dose (total daily dose (TDD): 100 mg)
- Children with BSA 0.33–0.54 m²: 100 mg per dose (TDD: 200 mg)
- CML resistant or intolerant to other treatments:
- Adults: 400 mg twice daily
Nilotinib Hydrochloride Potential Interactions with Other Medications
While Nilotinib hydrochloride delivers impressive results, its potency also raises concerns about potential interactions with other medications. Let’s explore this intricate landscape and equip you with knowledge for safe and effective treatment.
Types of Interactions
- Increased Nilotinib Levels: Certain medications can hinder the breakdown of nilotinib hydrochloride, leading to higher levels in your body and potentially intensified side effects. These include:
- Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors: ketoconazole, ritonavir, clarithromycin, grapefruit juice
- Antiretroviral medications: atazanavir, tipranavir, lopinavir/ritonavir
- Decreased Nilotinib Levels: Other drugs can accelerate the breakdown of nilotinib hydrochloride, diminishing its effectiveness. Examples include:
- Strong CYP3A4 inducers: carbamazepine, phenytoin, rifampicin, St. John’s wort
- Certain anticonvulsants: phenobarbital, phenytoin
- Additive Side Effects: Combining nilotinib hydrochloride with medications having similar side effects can amplify those effects. Examples include:
- Medications that increase bleeding risk (anticoagulants, aspirin)
- Medications that cause fatigue (muscle relaxants, antihistamines)
Conclusion
Nilotinib hydrochloride has emerged as a valuable therapeutic option in the treatment of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia, demonstrating efficacy in both treatment-naive and resistant/intolerant patients. Its targeted mechanism of action on the BCR-ABL fusion protein, coupled with its ability to induce apoptosis, makes it a potent weapon against CML. Regular monitoring and patient education are essential components of the comprehensive approach to nilotinib therapy, ensuring both therapeutic efficacy and patient safety. As the field of oncology continues to advance, targeted therapies like nilotinib contribute significantly to improving outcomes and the quality of life for individuals affected by CML.

Qingmu stands tall as a leading nilotinib hydrochloride manufacturer. Renowned for their unwavering commitment to quality and patient well-being, Qingmu employs stringent manufacturing practices and cutting-edge technology to deliver nilotinib of exceptional purity and efficacy. Their dedication extends beyond production, as they actively engage in research and development to refine nilotinib formulations and explore their potential in tackling other cancers. By prioritizing both the present and future of CML treatment, Qingmu empowers patients, clinicians, and the broader healthcare community to combat this blood cancer with confidence and hope.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be interpreted as medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of any medical condition.