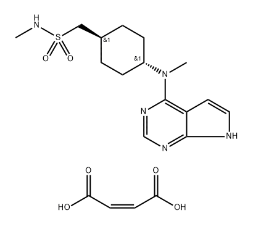
Ruxolitinib and its Phosphate Form: Exploring a Potential New Treatment Option
Ruxolitinib is a medication that has revolutionized the treatment of several blood cancers and related conditions. This article explores ruxolitinib, its current uses, and mechanism of action, and introduces the concept of ruxolitinib phosphate as a potential new form of the drug.
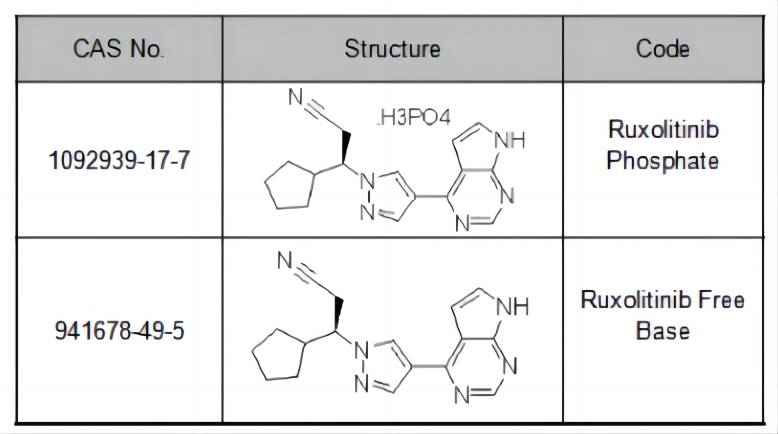
Ruxolitinib: A Targeted Therapy
Ruxolitinib is a small molecule inhibitor that targets a specific group of enzymes called Janus kinases (JAKs). JAKs are a family of enzymes involved in the signaling pathways of various cytokines, which are molecules that regulate cell growth and differentiation. In certain diseases, such as myelofibrosis and polycythemia vera, abnormal JAK activity contributes to uncontrolled cell growth and other disease processes.
Ruxolitinib works by selectively inhibiting JAK enzymes, thereby interrupting the signaling pathways that promote disease progression. This targeted approach offers a significant advantage over traditional therapies that may have broader effects and cause more side effects.
A. Current Uses of Ruxolitinib
Ruxolitinib has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of several conditions:
- Myelofibrosis: This is a rare bone marrow cancer characterized by excessive scar tissue formation in the bone marrow. Ruxolitinib has been shown to improve symptoms such as fatigue, splenomegaly (enlarged spleen), and bone pain in patients with myelofibrosis.
- Polycythemia vera: This is a blood cancer characterized by an overproduction of red blood cells. Ruxolitinib can help control the number of red blood cells and reduce the risk of blood clots associated with polycythemia vera.
- Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD): This is a serious complication that can occur after a stem cell transplant when the donated stem cells attack the recipient’s body tissues. Ruxolitinib is used to treat steroid-refractory acute GVHD, which means it is used in cases where corticosteroids, the first-line treatment for GVHD, have not been effective.
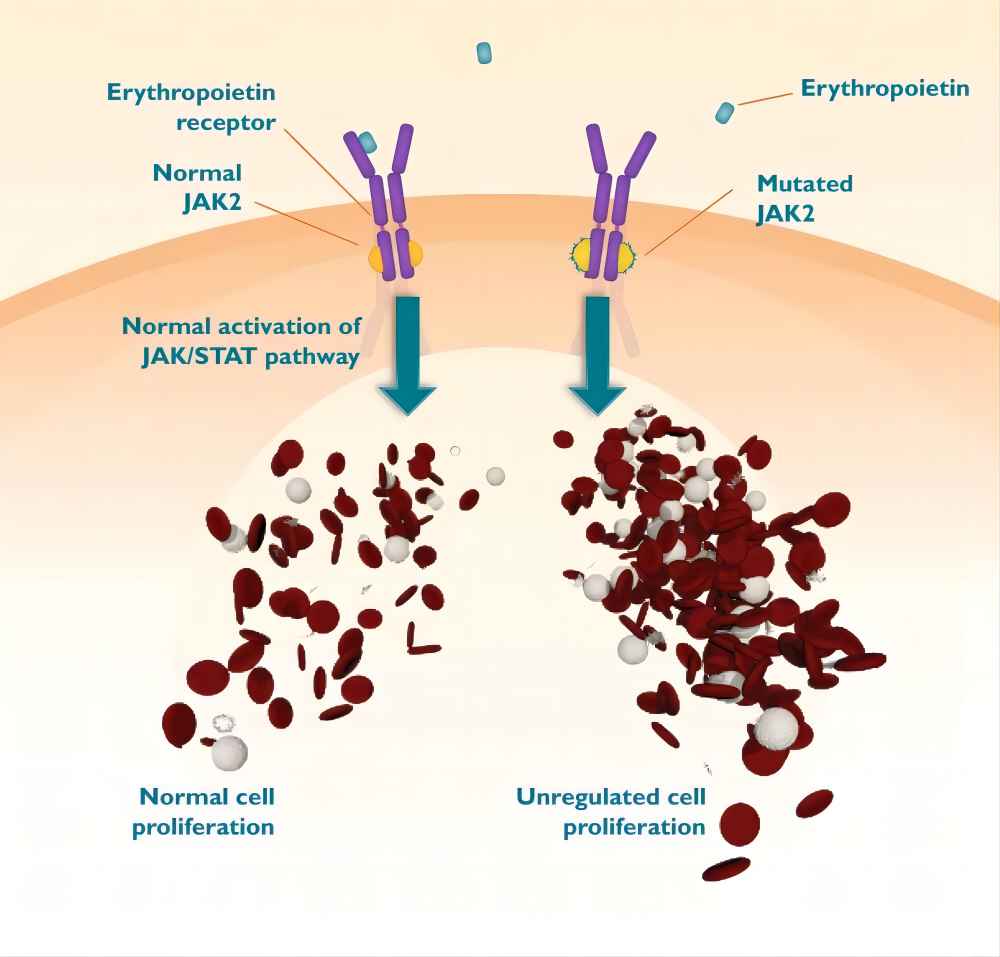
B. Mechanism of Action of Ruxolitinib
As mentioned earlier, ruxolitinib targets JAK enzymes. JAKs are involved in the signaling pathways initiated by various cytokines. These signaling pathways are crucial for normal cellular functions, but in some diseases, they become dysregulated, leading to uncontrolled cell growth, inflammation, and other pathological processes.
Ruxolitinib binds to the ATP-binding pocket of JAK enzymes, which is the region where JAKs interact with adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a molecule essential for their activity. By binding to this pocket, ruxolitinib prevents JAKs from binding to ATP and becoming activated. Consequently, the signaling pathways initiated by certain cytokines are disrupted, leading to reduced cell proliferation and other beneficial effects in the context of diseases like myelofibrosis and polycythemia vera.
Ruxolitinib Phosphate: A Potential New Form
Ruxolitinib phosphate is a potential new form of ruxolitinib currently under investigation. While the complete details of ruxolitinib phosphate are not yet publicly available, some information can be gleaned based on the concept of its phosphate form.
1. Properties of Ruxolitinib Phosphate
The addition of a phosphate group to ruxolitinib might alter its chemical and physical properties. The specific structure of ruxolitinib phosphate, if available from the ruxolitinib API information, would be crucial for understanding these changes. Potential modifications could include:
- Altered solubility: The phosphate group might influence the solubility of ruxolitinib phosphate in water or biological fluids. This could impact its absorption and distribution in the body.
- Changed ionization state: The presence of the phosphate group might affect the ionization state of ruxolitinib phosphate at different pH levels. This, in turn, could influence its interaction with biological membranes and its ability to enter cells.
2. Potential Advantages of Ruxolitinib Phosphate
Based on the theoretical properties of phosphate groups, ruxolitinib phosphate might offer some advantages over the current form of ruxolitinib:
- Improved bioavailability: The addition of a phosphate group could potentially enhance the solubility or absorption of ruxolitinib, leading to higher drug levels in the bloodstream and potentially improved efficacy.
- Targeted delivery: Phosphate groups can be used to attach targeting moieties to drugs. These moieties could help deliver ruxolitinib phosphate specifically to diseased cells, potentially reducing side effects on healthy tissues.
- Reduced side effects: By improving drug targeting or altering the pharmacokinetic profile (absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion), ruxolitinib phosphate might lead to a lower incidence or severity of side effects compared to the current form.
It is important to note that these are potential advantages based on theoretical properties. Extensive research and clinical trials are necessary to confirm these benefits and determine the safety and efficacy of ruxolitinib phosphate compared to the current form.
Comparison of Ruxolitinib and Ruxolitinib Phosphate
At this stage, a definitive comparison between ruxolitinib and ruxolitinib phosphate is not possible due to the limited information available on the new form. However, a table can be constructed to summarize the known aspects of each:
| Feature | Ruxolitinib (Current Form) | Ruxolitinib Phosphate (Potential New Form) |
| Chemical Structure | Known | Potentially modified with a phosphate group (specific structure might not be publicly available) |
| Mechanism of Action | Inhibits JAK enzymes | Expected to retain the JAK-inhibiting mechanism |
| Uses | Myelofibrosis, Polycythemia vera, GVHD | Potential use in the same or similar conditions, depending on clinical trial results |
| Bioavailability | Established | Potentially improved |
| Targeted Delivery | Not currently present | Possible with the addition of targeting moieties |
| Side Effects | Known profile | Potential for reduced side effects |
The Road Ahead: Research and Development
Ruxolitinib phosphate represents a promising avenue for further development in targeted therapies for myelofibrosis, polycythemia vera, and potentially other conditions. However, several key steps are needed before it can be considered for clinical use:
- Preclinical studies: Extensive in vitro and in vivo studies are necessary to evaluate the efficacy and safety profile of ruxolitinib phosphate. These studies will assess its activity against target cells, potential off-target effects, and potential side effects.
- Formulation development: The optimal formulation for ruxolitinib phosphate needs to be determined. This includes factors like dosage form, stability, and route of administration.
- Clinical trials: If preclinical studies are promising, well-designed clinical trials will be required to assess the safety and efficacy of ruxolitinib phosphate in humans. These trials will involve patients with the target conditions and will compare ruxolitinib phosphate to the current form or a placebo.
- Regulatory approval: After the successful completion of clinical trials, the data will be submitted to regulatory agencies like the FDA for review and potential approval. This process ensures the drug meets strict standards for safety and efficacy.
The timeline for these steps can vary significantly. However, the potential benefits of ruxolitinib phosphate warrant continued research and development to bring this new form to patients who could benefit from it.
Conclusion
Ruxolitinib has established itself as a valuable treatment option for several blood cancers and related conditions. Ruxolitinib phosphate represents a potential new form of the drug with exciting possibilities. Improved bioavailability, targeted delivery, and reduced side effects are some of the potential advantages this new form might offer. However, significant research is still needed to confirm these benefits and ensure the safety and efficacy of ruxolitinib phosphate. As research progresses, ruxolitinib phosphate could potentially become a valuable addition to the therapeutic arsenal for treating blood cancers and other diseases where JAK signaling plays a critical role.
References
- Verstovsek, S., et al. (2012). A small-molecule inhibitor of JAK1 and JAK2 signaling pathways in myeloproliferative disorders: Early clinical findings from a phase 1/2 trial. Leukemia, 26(8), 1804-1810. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22370700
- Lugo, T. G., et al. (2012). Janus kinase (JAK) pathway inhibition in autoimmune diseases and immunodeficiency. Leukemia, 26(1), 4-14. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21865987
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2021). Jakafi (ruxolitinib) tablets prescribing information. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2011/202192lbl.pdf